The History of Milk Caps, Menko, and POGs
Milk was first transported by railroad in 1835 . The first train shipments from Westborough, Massachusetts, travelled 32 miles to
Boston in baggage cars. To meet the growing demand of cities, ice-packed
railcars were designed for longer distances. The raw milk was commonly
delivered by horse-drawn wagons and ladled from casks or milkcans. The
consistency of cream varied for each customer. Each stop on a route increased
the risk of contamination.
Dairy distributors experimented with various methods to properly store and
transport a pure product. In April 1848,
Chambers's Edinburgh Journal reported that corked milk bottles had
remained preserved after eighteen months. On August 13, 1873, a milkman in
Elmira, New York, was reported to use pint and quart bottles that were
returned daily. The corked bottles were secured on racks mounted to the milk
wagon.
The first glass milk jar patent was issued to George Lester on January 29,
1878. The "Lester Milk Jar" was sealed with a screw-down clamp. In May 1879,
Echo Farm in Litchfield, Connecticut, delivered milk in tin-lid bottles
produced by Warren Glass Works. The "Warren Glass Bottle" was patented by
Louis Whiteman on March 23, 1880.
Harvey Barnhart and brother Samuel Barnhart patented a seated bottle opening
with a disposable fiber cap on September 17, 1889. "The Common Sense Milk Jar"
was marketed by the Thatcher Manufacturing Company in 1892. The first fiber
milk caps, or plugs, were soaked in paraffin wax.
The 1897 Sears Roebuck Catalogue lists two sizes of stoppers for "The
Common Sense Milk Jar." The "No. 2 Cap" has remained the most popular size throughout history, measuring approximately
1.625 inches (42 mm). Thatcher would reproduce dairy logos using
electrotyping. Printing was free with orders of 50,000 or more.
Advancements in pasteurization and commercial refrigeration allowed bottles to
be transported longer distances. By the turn of the century, the cardboard
milk cap cover had become the industry standard. Dairies and bottlers
distributed metal picks designed to pry the seated cap.
Many variations of the disk cover were created by competitors. A pull tab
bottle cap was first patented by Henry Bradley on August 11, 1908. The Bradley
design is made of two layers of glued pulpboard. A flexible thumb tab is cut
from the top layer.
On June 6, 1909, Frank L. Nichols patented a machine to cut, print, and staple
caps. The cap design includes a separate tab attached with a wire
staple. The pull tabs were commonly made of tough red-colored fiber. The
American Dairy Supply Company of Washington, D.C., marketed "The Cap with the
Red Flap" as "The Certified Cap." Health authorities protested the name for
misleading consumers. On February 21, 1923, the "The Certified Cap" trademark
renewal was denied by the Commissioner. The decision was successfully
appealed.
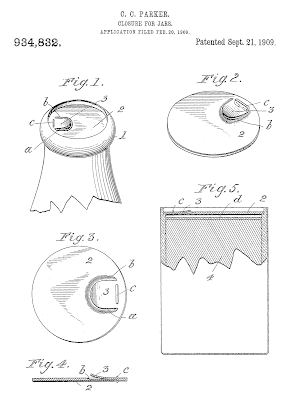
The most popular stapled cap design was first patented by Charles C. Parker on
September 21, 1909. The caps were cut from a single layer of 40-point sulfite
pulpboard and soaked in paraffin wax. The U-shaped tab is reinforced with a
wire staple. The "Perfection Pull Cap" was first produced by the Hagerstown
Cap Company in Maryland. The company printed dairy logos for free on orders of
50,000 or more. Two-color prints were available in red, blue, green, purple,
black, and brown.
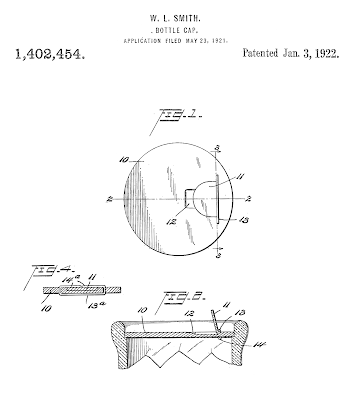
Variations of the "Perfection Pull Cap" were patented by Wilbert L. Smith and
Oren F. Baltzley in 1922. Smith was part owner of the Smith-Lee Company in
Oneida, and co-founder of the Smith Corona typewriter company. The new designs
included a recessed notch to allow for easier prying. The Smith design
features an extended wire staple to prevent tearing.
Milk cover games resemble the Japanese game of kamimenko (紙めんこ).
Kami means "paper" and menko means "small face." The origins are
traced back to anaichi, a coin throwing game played during the Edo period. Doromenko and
Keshi-men
made of molded clay were popular before the introduction of stamped lead
namari menko.
Paper menko appeared as shōya-ken and kitsune-ken (狐拳)
card games produced during the late Edo period. The ken games are
variations of "rock, paper, scissors" known as kitsune (fox),
ryōshi (hunter), and shōya (headman). In 1828, botanist
Philipp Franz von Siebold returned from Japan with shōya-ken painted
on wooden cards. Early Meiji era examples are painted on layered
washi paper.
An English paper machine was imported to Ōji in 1873 and a mechanized mill opened on December 16, 1875. Shoshi Kaisha, later
known as Ōji Paper, began producing sulfite wood pulp in 1889. Taro Naruse, a toy
merchant in Nagoya, first sold shōya-ken images on pulp paperboard
around 1892. The woodblock-printed cards were sold in two square sizes
that measure 2.5 cm and 5.5 cm.
Around 1894, Isaku Miki began manufacturing kamimenko in Osaka. A
player places menko cards on the ground and an opposing player throws
another menko, winning any pieces that have overturned. Some children
would cut the square corners to create an octagonal shape, leading to the
creation of round game disks. The first baseball menko is an anonymous player on a disk from 1897. Rectangular menko cards became common
following the nationalization of cigarettes in 1898.
The Japan Home Ministry banned lead from all toy manufacturing in 1900.
The shift from lead-based products and the introduction of machinery
helped the paper menko industry to flourish. Early 20th century menko
feature a wide variety of illustrations that include samurai, soldiers,
and sumo wrestlers. The "fox, hunter, shōya" images were gradually
replaced by "rock, paper, scissors" hand symbols.
Cigarette insert cards were introduced in April 1877 by New York
manufacturer Thomas H. Hall. In March 1889, The San Francisco Examiner
reported that local children were playing a card-throwing game called
"Crusoe." Each player tosses or shoots a tobacco card, trying to land near
a mark. The closest player "picks up all the cards and flops them into the
air. All that land face uppermost belong to him if he calls 'heads' and
vice versa, and the next boy has a chance to throw whatever cards remain."
Cigarette card games were played across America under various names including
"flipping," "scaling," or simply "cards." Games were commonly wagered for
pennies or "keepsies."
On February 7, 1903, The Evening Star reported that children in
Washington, D.C., and Philadelphia were playing "milktops." The game had
reached D.C. sometime before Christmas of 1902. Boys were
commonly seen following dairy wagons to ask customers for the covers. Only caps printed with
dairy names were desired and some could sell for a penny each. The Evening Star wrote, "They are thrown on the ground, and those
that fall with the printed side on top win."
On February 4, 1906, The Washington Times reported that milk tops
were more popular than cigarette cards and postage stamps. Milk cap
gambling had been banned by several D.C. public schools. On February 24,
The Evening Star noted that milk and cream tops from smaller
dairies carried more value. "They toss them in the air, so that by this
game of chance they lose or win heavily."
In April 1908, it was widely reported that ten-year-old Quentin Roosevelt,
son of President Theodore Roosevelt, had traded White House garden roses
for milk caps. The Columbus Journal wrote, "The children have a
game which they play by means of these disks, and, moreover, certain
prestige attaches to the boy who can show the longest string of 'milk
tops'."
According to traditional accounts, immigrants on Maui plantations played
milk cover games in the early 1920s. Some Filipino residents referred to
the game as pachi. The milk covas are stacked in a vertical
tower, each facing the same direction. A player throws a kini, or
slammer cap, and wins any caps that have overturned. A thumb tab can
produce a random spring element.
The kini, or keni, was often made by gluing together two or three milk caps.
Kini is short for kinikini, a Ni'ihau name for the seeds of
Kākalaioa that means "abundant." The medicinal
Guilandina bonduc is a thorny bush native to Tonga, commonly known
as nickernut, nicker bean, or Hawaiian pearls. The yellow flowers produce
pods that contain two glossy, spherical seeds measuring roughly 15–20 mm
in diameter. The hard seeds were commonly used as marble shooters by
children throughout Polynesia.
A photograph of two Los Angeles children playing milktops was published in
the September 1931 issue of
Camera Craft: A Photographic Monthly. "Milk Tops" by Hideharu
Fukuyama won second place in the September Advanced Competition. A gelatin
silver print is held by the Yokohama Museum of Art in Japan.
As the US prepared to enter
World War II in
1941, Roberts Dairy of Nebraska issued the first collection of Superman
milk caps for the
Roberts Superman Defense Club of America. Roberts later produced a series of twenty "Code Note" caps for the
Supermen of America
organization. Each full set of caps could be redeemed for premium prizes.
The demand for home milk deliveries steadily declined in the post-war era.
In 1940, about 45% of American households owned a refrigerator. By 1960,
ownership had increased to over 80%. Pure-Pak cartons and plastic
containers had widely replaced glass for all milk packaging. The
last known horse-drawn milk wagons in America were operated by Goshen Dairy in Philadelphia and S.C. Price
Dairy Farms in Hazleton, Pennsylvania. Goshen Dairy ended horse deliveries in March 1972. Price's Dairy maintained Belgian Draught horses as late as 1973.
The POG tropical juice drink was created by Mary Young Soon, a food
product consultant at Haleakala Dairy in Kahului, Maui. POG is an acronym
for passion fruit, orange, and guava. The fruit combination has been a
popular Hawaiian beverage since the 19th century. Frances "Effie" Cameron,
daughter of board member Colin Cameron, is credited for naming the drink
POG. The trademark application lists the date of first use as November 2,
1970. The POG trademark was filed on December 15, 1972, and registered on
January 22, 1974.
In August 1984, collector Vance Cannon created a milk cover exhibit for Ali'iolani School reunions. Cannon placed a notice in the Honolulu-Star Bulletin looking for other collectors. The reunion committee used milk covers for older alumni to become reacquainted. The game began a small revival on the islands.
The POG trademark was transferred to the Baldwin Pacific Corporation in
1986. Haleakala Dairy began distributing "'Milk Cap Cover' game" caps for
Mountain Fresh Milk and POG juice. The caps were printed by Stanpac Inc.
in Smithville, Ontario. Stanpac operated "Perfection Pull Cap" machines
manufactured in the 1930s. The two-color disks are tabbed, stapled and
waxed. Each cover measures approximately 1.625 inches (42 mm), the
original "No. 2" size for Thatcher milk bottles.
The POG marketing campaign was headed by Charlie Nalepa. The Pogdlodyte mascot, originally the Izard of POG, was created by Nalepa and a Walt Disney designer. The surfing Poglodyte displaying a shaka sign was trademarked by Orchards Hawaii, Inc. on July 12, 1988.
Blossom Iwalani Galbiso was a guidance teacher at Waialua Elementary
School on Oahu. After observing an aggressive playground match of sham-battle,
Galbiso wanted to introduce a safe, but challenging activity. Galbiso
played milk covers as a child and she had previously seen caps being used
at another school.
In April 1991, Blossom Galbiso's daughter purchased two tubes of POG
covers and two tubes of Mountain Fresh covers from Haleakala Dairy on
Maui. The caps were used for various math lessons and classroom
activities, but the old game was immediately popular with students.
According to Galbiso, "Something magical occurred and the students were
hooked."
Blossom Galbiso wrote, "Although I had introduced the game as 'milk
covers' they favored the red POG design from Haleakala Dairy and hence
renamed the game 'POGs'." In March 1992, the First Annual Milk Cap
Tournament was held at Waialua Elementary. By May, Haleakala Dairy was
selling 25,000 caps a month to customers on the North Shore.
Nostalgia from older generations helped the revival to spread. Branded
caps from schools, businesses, and events were soon being distributed
throughout the islands. Copycat disks with unlicensed images and
holographic foil pieces appeared from local printers, California, and
Taiwan.
In January 1993,
SkyBox
trading card representatives took notice of the game while attending an
industry convention in Honolulu. In March, the company began marketing
DC Comics SkyCaps
with a promotional sheet for the
"Reign of the Supermen!"
story arc. Sample packs of various "SkyCaps" licenses were
distributed at the 14th National Sports Collectors Convention in Chicago
from July 22–25, 1993.
Throughout the summer of 1993, Stanpac was shipping roughly four million
POG juice caps per week. Stanpac was the sole producer of "Perfection
Pull Caps" in North America and the company continuously operated six machines
to fulfill the growing demand. Stanpac employees learned the game
from a videotape sent by Blossom Galbiso. Stanpac owner Steve Witt would
visit Galbiso in Waialua. Witt printed a limited collection of 2,000
Canada and US flag caps to raise money for Waialua Elementary.
"Mother of the Milk Cap Revival" caps featuring Blossom were commissioned by her husband Frank Galbiso
in the summer of 1993. The "Mother of POGs" passed away on December 27,
1994, at the age of 45.
POGs became a generic term for the disks and the game itself. In
September 1993, Armor All founder Alan Rypinski purchased the POG
copyright and trademark from Haleakala Dairy. Rypinski established The World POG Federation (WPF) and the
"old-fashioned game of the future" exploded as a global marketing
phenomenon. The Poglodyte mascot was redesigned as Pogman. In November 1994, Rypinski settled an agreement to retain
exclusive rights to the POG name.
POG The Game was released by Milton Bradley in 1994. POGs were
officially licensed by Canada Games, Animage in France, and Waddingtons in
the UK. An official POG measures approximately 1.625 inches (42 mm) in
diameter, the original "No. 2" size from Thatcher. The back of each
official product contains the World POG Federation logo or Milkcap Maker
trademark.
POG Classics feature 60 designs printed on waxed, two-color
"Perfection" milk caps manufactured by Stanpac. Designer POG Milkcaps are
multicolor disks printed on white cardstock without thumb tabs, staples,
or wax. The official POG KINI are made of Ryton polyphenylene
sulfide, a flame-resistant and chemical-resistant thermoplastic. Each
POG KINI is mold-injected and decorated with holographic foil. The
POG Slaminator slammers are stamped into anodized aluminum disks.
Billions of similar disks were produced including Gops,
Flippos, TROVS, and Slammer Whammers. Serrated disks
known as Tazos were sold by PepsiCo and Frito-Lay in South America.
McDonald's packaged McCaps inside of Happy Meals.
Nintendo Power distributed
Super Power Club Caps
with the monthly magazine. Marvel Comics produced Hero Caps
and
Todd McFarlane
sold Spawn caps as Spogz.
McDonald's, Nintendo, and Marvel would later distribute officially
licensed POGs. Other major partners included Coca-Cola, Disney, Keds,
Mattel, and Knott's Berry Farm. Official POGs were produced for the White
House Easter Egg Roll on April 17, 1995.
Comedian Steve Allen is depicted as "Inventor of the POG" in
The Simpsons episode "'Round Springfield," first aired on April 30, 1995.
Milhouse trades Bart's soul for a collection of ALF POGs in "Bart Sells
His Soul," first aired on October 8, 1995. "Remember ALF? He's back, in POG
form."
The milk covers game received criticism from parents due to the gambling
mechanics involved. Teachers voiced concerns of the game causing
distractions, arguments, and thefts. In 1994, games for cash and
pornographic disks were reported at a Los Angeles middle school. By
1997, the game was banned by various schools in the US, Australia,
Canada, Germany, Iceland, Sweden, and UK.
Approximately ten billion collectible cardboard disks were sold
worldwide from 1994–1998. The POG craze had faded by the end of the
millennium, coinciding with the crash of the comic book and trading card
industries.
In January 1999, Haleakala Dairy was sold to Meadow Gold Dairies,
originally known as the Honolulu Dairyman's Association. In April 2020,
Meadow Gold was purchased by Hawaii dairy farmer Bahman Sadeghi. The
company continues to produce the POG tropical juice drink.
In 2005, Funrise Toys licensed the POG brand in an attempt to evoke consumer nostalgia. POGs were showcased as a 1990s fad in
American Pie Trading Cards, released by The Topps Company in 2011.
POGs: The Official Mobile Game was announced as an Indiegogo crowdfunding campaign on June 3, 2018. The World POG Federation returned in February 2021, and the brand continues
to distribute official POG game pieces. Stanpac no longer produces the
"Perfection" milk caps. In April 2022, The WPF began issuing POGART,
original POG designs rendered as digital
non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
-
"Agreement Puts an End To 'Pog' Trademark War."
The New York Times, 9 November 1994.
"A new fad is now raging among the boys of the city."
The Evening Star, 24 February, 1906, p. 2.
Andaya, Leonard Y. "From American-Filipino to Filipino-American."
Social Progress in Hawaii, vol. 37, 1996, p. 105.
"An Elmira milkman has introduced a novelty..."
Lewis County Democrat, 13 August 1873. p. 2.
Baltzley, Oren F.,
"Bottle-cap machine."
US Patent 1,415,507. 9 May 1922.
Barnhart, Harvey P., and Samuel L. Barnhart.
"Means for capping and sealing milk-bottles."
US Patent 411,368. 17 September 1889.
Bradley, Henry.
"Bottle and Jar Closure."
US Patent 895,719. 11 August 1908.
Cekola, Anna,
"O.C. Schools Are Banning Popular New Game Craze."
Los Angeles Times, 7 February 1994.
"Collections of milktops is the new thing under the sun..."
The Evening Star, 7 February 1903, p. 18.
Creamer, Beverly. "Founder of milk cap craze embarrassed by her fame." The Honolulu Advertiser, 30 May, 1993, p. 7.
DeForest, Heman Packard, and Edward Craig Bates.
The History of Westborough, Massachusetts.
Westborough, The Town, 1891. pp. 351—352.
DeRolf, Shane. The Official POG Milkcap Collector's Guide.
Random House Children's Books, 1995.
Doheny, Kathleen.
"POGs: Kids are Flipping their Lids."
The Washington Post, 6 September 1994.
Engle, Murry.
"Big Island man says he revived the latest craze."
Honolulu Star-Bulletin, 21 February 21, 1993, p. F8.
Essoyan, Susan.
"New wave of 'pog' mania crests over Hawaii."
Los Angeles Times, 7 June 1993.
"F. R. Starr. of Echo farm, Litchfield..."
Connecticut Western News, 21 May 1879, p. 2.
Fukuyama, Hideharu. "Milk Tops."
Camera Craft: A Photographic Monthly, vol. 38, no. 9, September
1931, p. 443.
Galbiso, Blossom. "POGMANIA... The Rebirth of a Childhood Game..."
Milk Cover Collector, no. 1, AC Comics, March 1993, pp. 4–5.
"Glass in Dairies."
Chamber's Edinburgh Journal, no. 233, April 1848, p. 240.
Hoover, Will. "POGS: Crazy for milk caps."
The Honolulu Advertiser, 6 January 1993, pp. E1, E3.
Hurd, Duane Hamilton.
History of Worcester County, Massachusetts: With Biographical
Sketches of Many of Its Pioneers and Prominent Men, Volume 2.
J.W. Lewis & Company, 1889, pg. 1351.
Ishii, Yutaka. "Development of the pulp and paper industry in Japan
and the importation of pulpwood."
The Current State of Japanese Forestry: Its Problems and Future, vol. 7, 1991, pp. 1–6.
Johnson, Greg.
"Hoping to Milk Profits From Craze."
Los Angeles Times, 3 March 1994.
Lester, George H.
"Milk Jar and Can."
US Patent 199,837. 29 January 1878.
Linhart, Sepp, and Sabine Fruhstuck, editors.
The Culture of Japan as Seen Through Its Leisure. State
University of New York Press, 1998, pp. 334–341.
Milk Dealers' and Dairymen's Supplies. The Lakeside Press,
1890.
"'Milk Tops' Buy White House Roses."
The Columbus Journal, 29 April 1908, p. 3.
"Nalepa, 76, popularized POG."
The Maui News, 12 August 2014.
Nichols, Frank L.
"Machine for Making Cover or Closing Disks."
US Patent 927,002. 6 July 1909.
Parker, Charles C.
"Closure for Jars."
US Patent 934,832. 21 September 1909.
Sears, Roebuck and Company. 1897 Sears Roebuck Catalogue.
Chelsea House Publishers, 1968, p. 145.
"Shoya Ken."
Japan Playing Card Museum.
Smith, Wilbert L.
"Bottle Cap."
US Patent 1,402,454, May 23, 1921.
Sugitani, Shuichi. "The symbolization process of Shoyaken - Focusing
on the relationship with Shimenko."
Bulletin of Seinan Jo Gakuin University, vol. 14, 2010.
Taylor, Lois.
"All Hail Aliiolani."
The Honolulu Advertiser, 29 July 1984, p. C1.
"The Game Called 'Crusoe,' and How the Gamins Play It."
The San Francisco Examiner, 30 March 1889, p. 4.
"The Small Boy's Mania." Charlotte Daily Observer, 9 August 1909, p. 5.
"Two Splendid Articles for the Dairy." The Rural New-Yorker,
vol. 51, no. 2197, 5 March 1892, p. 163.
"Vance Cannon is trying to locate collectors of 'milk covers.'"
Honolulu Star-Bulletin, 15 August 1984, p. F-2.
"Washington Lads Collect Milk Tops."
The Washington Times, 4 February 1906, p. 4.
Watanabe, June.
"Going POG Wild!"
The Honolulu Advertiser, 31 May 1992, p. E4.
Whiteman, Louis P.,
"Jar for Milk &c."
US Patent 225,900. 23 March 1880.
Yale, Diane. "Horse-drawn era ended with Goshen Dairy fire." The Daily Reporter, 30 January 1973, p. B-3.







.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)




.png)
.png)

.png)





